Root Cause Analysis - Powerful Problem Solving Method
To find out the solution to a problem, we need to go to its root.

Every event has a cause or set of causes; if its cause occurs, then the effect must follow.
The dictionary defines “root cause” as the fundamental cause, basis, or essence of something, or the source from which something derives. Whether you are working in science, medicine, business, history..., tracing an event to its origins is the key to understand it.
Root Cause Analysis, simply as its name says, is a problem solving method that aims at identifying the root causes of problems. It is based on the principle that problems can best be solved by correcting their root causes, whereas correcting a causal factor that is not a root cause, though it would benefit the outcome, it does not prevent the recurrence of the problem within certainty. Nor does it prevent the occurence of another undesirable event within the same problem-fault-sequence.
Benefits of Root Cause Analysis
RCA saves time. Therefore it saves money and other resources. You don’t spend months and months working on something that doesn’t need fixing. Instead, you only fix the most important issues. Moreover, it uncovers relationships between causes and symptoms of problems, works to solve issues at the root itself and provides tangible evidence of cause and effect and solutions. Finally , RCA helps you to implement permanent and lasting solutions to prevent future issues.
Root Cause Analysis Process
- Define the problem.
- Collect Data - Gather information, data and evidence.
- Identify Possible Causal Factors - All issues and events that contributed to the problem.
- Determine root causes.
- Identify recommendations for eliminating or mitigating the reoccurrence of problems or events.
- Implement the identified solutions.
Root Cause Analysis Tools
-
5 Whys
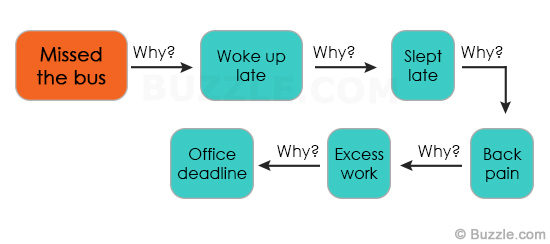
A simple problem-solving technique that helps users get to the root of the problem quickly. It was made popular in the 1970’s by the Toyota Production System. This strategy involves looking at a problem and asking “why” and “what caused this problem”. Often the answer to the first “why” prompts a second “why” and so on—providing the basis for the “5-why” analysis.
-
Fishbone diagram

Or Ishikawa Diagram — Derived from the quality management process, it’s an analysis tool that provides a systematic way of looking at effects and the causes that create or contribute to those effects. Because of the function of the fishbone diagram, it may be referred to as a cause-and-effect diagram. The design of the diagram looks much like the skeleton of a fish—hence the designation “fishbone” diagram.
-
Tree Diagram

-
Fault Tree Analysis

The event is placed at the root (top event) of a “tree of logic”. Each situation causing effect is added to the tree as a series of logic expressions.
-
Flow diagrams

Other methods:
- Scatter diagram
- Control Chart
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
- Barrier Analysis
- Pareto Analysis
- Kepner-Tregoe technique
RCA is a process that introduces organizational improvements in many situations, lasting improvements and most importantly, a learning process to follow for thorough understandings of relationships, causes and effect and solutions. By practicing RCA, you eliminate taking action on possible causes, and delay a response to the last responsible moment when the actual root cause of an effect is identified.
Keeping Your Tradeshow Relevant in the Future
This article is heavily based on Francis J. Friedman's "The Modern Digital Tradeshow", that can be downloaded for free on...
What Do Great Leaders Have in Common?
From ancient to modern, all great leaders share common key denominators.
How to Deal With An Incompetent Boss
An incompetent boss can seriously damage or derail your career, how to handle him/her?















